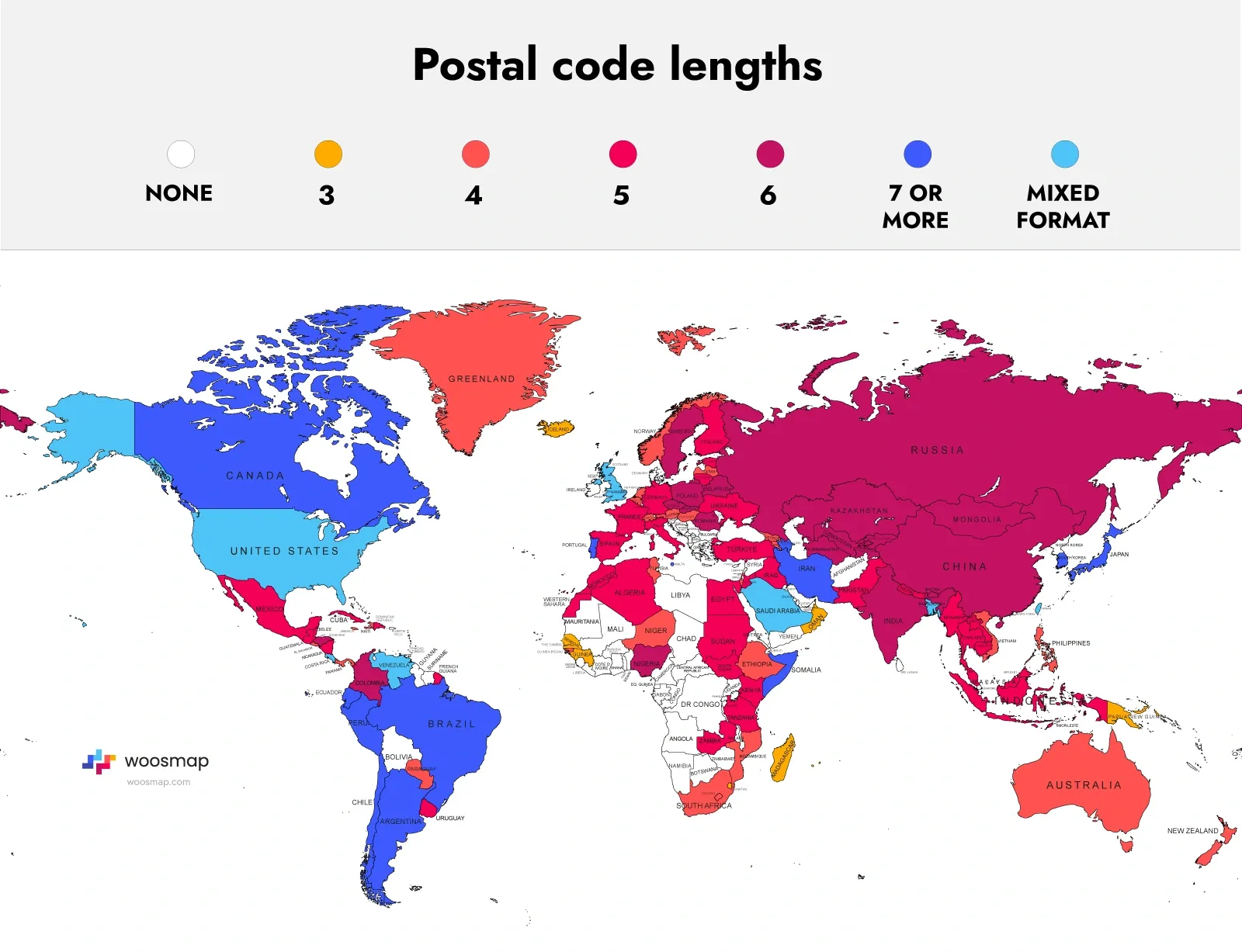
What are Postal Codes?
Postal codes are more than just a series of numbers and letters added to an address. They serve as vital tools for organizing and directing the flow of mail within specific zones and cities, but their significance extends far beyond this basic function. Understanding postal codes is essential for businesses operating online, as these codes play an essential role in commerce, security, data analytics, navigation, and many other aspects of modern life and business operations globally.
This article will explore the full scope of postal codes, their different types and formats, applications across various business groups, and the technological advancements that continue to expand their utility. These codes are crucial for postal services like the USPS in the United States across all states and districts to manage efficiently the complexities of the global shipping industry, with systems such as ZIP codes and postcodes enhancing mail delivery accuracy. Furthermore, postal codes serve as a key component in ensuring the precision of geolocation technology, which subsequently supports the delivery of goods and services in an increasingly digital economy.
Understanding Postal Codes
A postal code is a sequence of characters—numbers, letters, or both—assigned to geographic areas such as city, state, or district to facilitate mail sorting and delivery. Understanding these zones is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. While their primary purpose is to ensure efficient mail delivery, postal codes are also used in many other domains:
- E-commerce: Postal codes help determine shipping costs, estimate delivery times, and validate billing addresses to prevent fraud. In addition to traditional roles, postal codes can reduce the likelihood of unauthorized online transactions by matching billing addresses with cardholder information during credit card purchases.
- Marketing: Businesses use postal codes to segment and target audiences based on geographic or demographic information.
- Data Analytics: Governments and organizations use postal code data to identify health trends, like tracking disease outbreaks, optimize resource allocation for emergency services, and target infrastructure investments, such as building new schools or hospitals in high-growth areas. Additionally, postal codes' integration with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) enhances planning and response strategies in various sectors.
Postal codes are integral not only for traditional postal services but also for a range of modern applications, including online business services that support various aspects of everyday life and commerce. Their utility extends into geolocation services, security protocols, and public administration, showcasing their evolution from simple mailing aids to powerful tools in data management and digital transactions. Moreover, postal codes also allow postal workers to handle the increasing volume of mail more efficiently, which is crucial in populous regions and large cities where delivery routes are more complex.
Furthermore, worldwide systems, such as the Intelligent Mail Barcode and ZIP codes used by USPS in the United States, help optimize sorting processes to ensure quick and precise mail delivery. The efficiency of these codes is vital for maintaining timely and accurate delivery services, especially given the rapid increase in global e-commerce activities that rely heavily on robust postal code systems for cross-border transactions within various zones.
A Brief History of Postal Codes
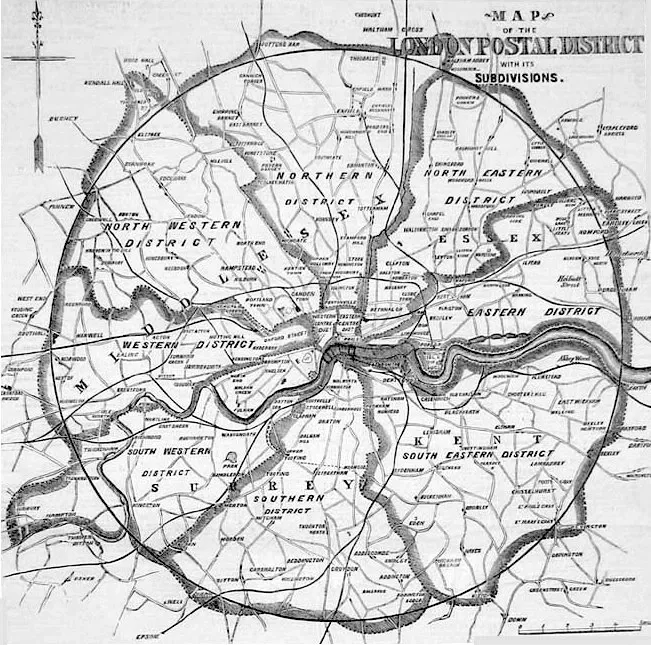
The concept of postal codes originated from the need to efficiently manage mail delivery as cities expanded and populations grew. One of the earliest systems was introduced in London in 1857, where the city was divided into ten districts to streamline mail sorting and delivery. This system laid the groundwork for the postal code systems used today.
Early Developments
In 1963, the United States introduced the ZIP code (Zone Improvement Plan), which greatly enhanced mail sorting efficiency by using a five-digit code that identifies a specific delivery area within a city or zone.
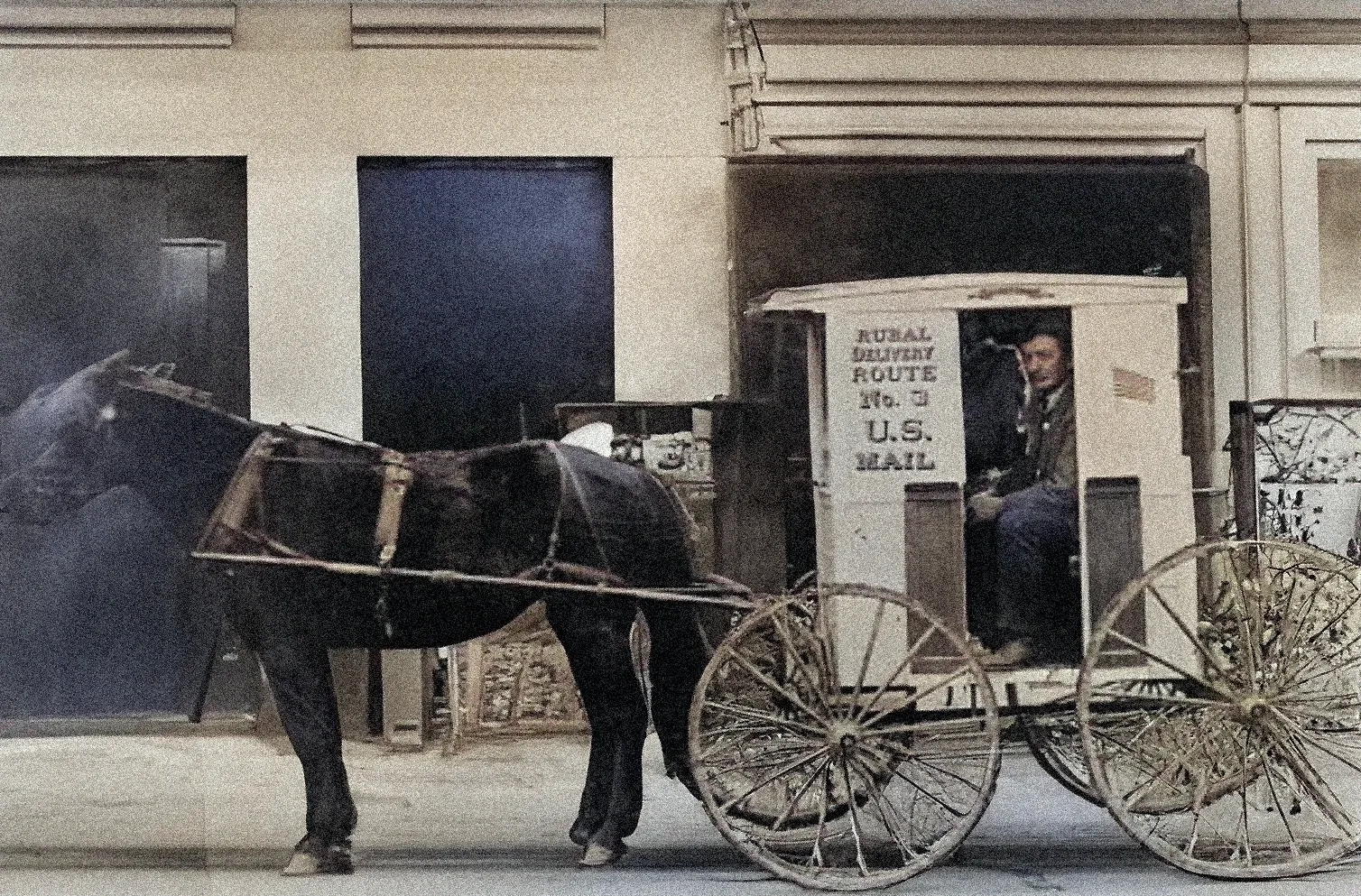

The ZIP code system was further refined in 1983 with the introduction of the ZIP+4 format, which adds four digits to the original five-digit code, allowing for even more precise location identification down to individual buildings, post office boxes, or floors within a building. This enhanced format improved mail delivery accuracy and reduced delivery times significantly, benefiting both businesses and consumers within specific zones.
Evolution in Different Regions
- Japan: Japan introduced its postal code system in 1968. The Japanese postal code consists of seven digits. The first three digits indicate the region, while the remaining four specify the local area or block. This detailed segmentation allows for efficient and accurate mail delivery even in densely populated cities like Tokyo.
- Germany: Germany introduced a postal code system during World War II to facilitate Germany introduced a postal code system during World War II to facilitate military communication and logistics. In 1993, after the reunification of East and West Germany, the system was standardized into a five-digit format to unify the postal operations across the country.
- France: France uses a five-digit postal code format where the first two digits represent the département (a regional division), and the last three digits specify the local post office. This system supports efficient mail routing and sorting in both urban and rural areas.
Different Formats of Postal Codes
Postal codes come in various formats depending on the country and its specific needs, such as assigning them to specific cities, states, or geographic zones. Some are strictly numeric, while others combine numbers and letters. Here are some of the most common formats:
Numeric Postal Codes
Common in countries like the United States, Japan, and France, numeric postal codes are straightforward sequences of numbers. In the U.S., ZIP codes consist of five digits, assigned to specific states, with an optional four-digit extension to specify more precise locations. Japan's system uses seven-digit numeric codes where the first three digits represent a regional area and the remaining four provide further specificity down to individual blocks or buildings.
Numeric codes are often easier for machine reading and processing, which makes them suitable for large-scale postal systems. These systems rely on automated sorting machines that quickly read numeric codes and direct mail to the appropriate distribution centers.

Alphanumeric Postal Codes
Alphanumeric postal codes, such as those used in the UK, Canada, and the Netherlands, combine letters and numbers to offer greater specificity. For example, "SW1A 1AA" in London pinpoints a location down to the street or building level, while Canada's "K1A 0B1" format provides similar precision. These codes are designed to maximize the amount of information conveyed in a small space, making them particularly useful in densely populated urban areas and various business zones.
Alphanumeric codes also help to avoid ambiguities that might arise with purely numeric systems. For example, mixing letters and numbers can increase the number of unique codes available, which is particularly important in regions with high population densities.
Variable-Length Postal Codes
Some countries use postal codes of varying lengths to accommodate different regions' needs, such as assigning them to specific cities, states, or districts. For example, Ghana uses codes ranging from five to seven characters, allowing flexibility for urban and rural areas. This flexibility helps accommodate the diverse geographic and demographic landscape of such countries, ensuring that each region has a postal code format that matches its specific requirements.
Variable-length codes can also be tailored to local administrative divisions and assigned to specific zones, providing a more intuitive system for local residents and postal workers. They allow postal authorities to adjust the level of detail provided by the code depending on the density of the population and the complexity of the local geography.
Special Postal Codes
Special codes are used for unique purposes. France's CEDEX system is designed for businesses receiving high volumes of mail, while Ireland’s Eircode assigns a unique identifier to each address. These systems cater to specific needs, such as ensuring that bulk mail is efficiently sorted and delivered or providing exact addresses for emergency services and delivery companies.
Ireland’s Eircode, for example, uses a system where each address or delivery point has a unique code, eliminating the confusion of similar addresses and ensuring precision in both urban and rural settings. This level of detail is especially important for emergency services, where every second counts, and accurate location data is critical.
If you need to find your Eircode, try our Woosmap Eircode Finder for quick and easy results.

The Role of Postal Codes in Modern Applications
Postal codes are much more than mere location identifiers; they play a vital role in many areas beyond mail delivery:
E-commerce and Fraud Prevention
Postal codes are integral to online Postal codes are integral to online shopping and security. They help calculate shipping costs, determine product availability, and prevent fraud by verifying that the billing address matches the information on file with the card issuer. The Address Verification System (AVS) is often used to authenticate transactions, reducing fraud risks. AVS cross-references the entered postal code with the one on file at the cardholder's bank, adding an additional layer of security to prevent unauthorized credit card purchases.
E-commerce platforms like Amazon and eBay rely heavily on postal codes to optimize their delivery networks. By analyzing postal code data, these platforms can determine the most efficient routes within specific zones, reduce delivery times, and minimize shipping costs. This is particularly important in regions with complex urban layouts or where delivery infrastructure is still developing.
Additionally, businesses use postal code information to enhance their address autocomplete features, which streamline the buying process by quickly suggesting and verifying addresses for customers.
Address Validation and Geocoding
Postal codes play a crucial role in address validation. Address validation software checks postal codes and states against authoritative databases to ensure the accuracy of addresses. This is essential for businesses that depend on reliable address data to maintain customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. By verifying addresses before dispatch, businesses can reduce the number of undeliverable shipments, save on costs, and enhance customer experience.
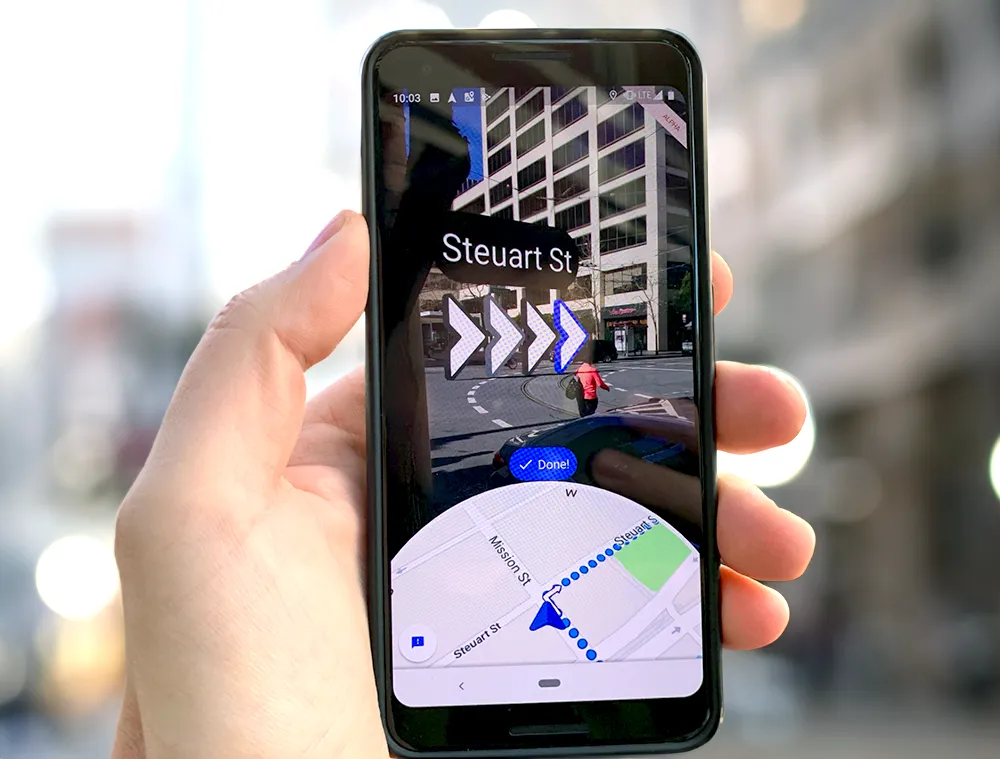
Geocoding is another modern application where postal codes are converted into geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude). This is crucial for navigation, mapping, and location-based services. Ride-hailing apps, for instance, use geocoding to match drivers with passengers based on their postal codes, optimizing routes within specific zones to delivery points and improving service efficiency. Services like Woosmap’s postcode and address finder provide advanced tools to enhance address lookup capabilities, improving the accuracy and speed of deliveries.
Rooftop geocoding takes this a step further by pinpointing the exact building, which is vital for precise deliveries within specific business zones and city areas. It allows for highly accurate deliveries, especially in dense urban environments where multiple buildings can share similar addresses.
Address Parsing and Standardization
Address parsing breaks down an address into its components, like street number, street name, city, state, and postal code, ensuring it conforms to postal standards. This process involves separating each part of an address into discrete fields that can be individually analyzed and validated.
Address Standardization involves formatting and editing the address according to a country's postal rules, reducing delivery errors, and improving mail accuracy. Standardized addresses help in reducing undelivered mail due to incorrect or non-standard address formats. This is particularly important for businesses sending out bulk mail or packages, as even small errors in address data can lead to significant operational inefficiencies.
Address parsing and standardization are crucial in maintaining large and archived address databases, ensuring that data is kept clean, up-to-date, and useful for a range of business applications.
Marketing and Public Services
Postal codes are used extensively in targeted marketing and public service planning. Businesses analyze postal code data to tailor marketing efforts based on the demographics and consumer behaviors associated with different districts and zones. For example, a company might target high-income postal code areas with luxury products, while more budget-friendly options might be marketed in other areas.
Governments use postal codes for resource allocation, emergency response, and public health planning. By understanding the distribution of resources and population density within specific postal zones, authorities can make better decisions about where to allocate services such as hospitals, schools, and fire stations across different states or cities.
Public health agencies often rely on postal codes to track the spread of diseases, target areas for vaccination campaigns, or allocate resources during health emergencies. Postal codes provide a granular level of detail that can make public health interventions more effective and targeted within specific zones.

Technological Advances in Postal Code Systems
Modern postal code systems are increasingly integrated with advanced technologies, enhancing their accuracy and efficiency.
Intelligent Mail Barcodes (IMb)
The USPS uses Intelligent Mail Barcodes (IMb) to encode information, including ZIP code data, into a machine-readable format. This technology allows for faster, more accurate sorting and delivery of mail within specific postal zones, reducing labor costs and minimizing errors. The IMb contains much more information than traditional barcodes, such as delivery route details, including assigned routes or zones, customer information, and other tracking data, providing end-to-end visibility in the mail stream.
IMb technology supports advanced features such as delivery confirmation and automated redirection if a package or letter is mistakenly routed. It also enhances customer experience by allowing real-time tracking updates and notifications about delivery status.

Enhanced Geocoding Techniques
Advanced geocoding techniques, such as rooftop geocoding, convert postal codes into exact geographic locations down to the individual building or unit level within specific city zones. This precision is essential for logistics companies that need to optimize delivery routes or locate specific addresses in dense urban environments. Enhanced geocoding can reduce delivery errors, save time and fuel, and provide better customer service by ensuring that parcels reach their intended destination without unnecessary delays.
Technologies like Geospatial Information Systems (GIS) integrate postal code data with maps and satellite imagery, providing detailed insights into traffic patterns, urban development, and regional planning. Such systems are increasingly used in disaster response planning, where precise location data can save lives by guiding emergency responders to affected areas efficiently.
Machine Learning and AI
As machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies advance, postal codes are likely to play an even more significant role in optimizing logistics and supply chain operations. AI can analyze postal code data to predict demand patterns, optimize delivery routes within specific zones, and identify areas for service improvement based on assigned postal zones.
For instance, AI-driven predictive models can forecast the number of deliveries expected in a given postal code area on specific days, allowing logistics companies to allocate resources more effectively. Additionally, ML algorithms can detect patterns in delivery delays or errors, helping companies refine their processes and reduce costs.
Blockchain for Postal Code Security
Blockchain technology offers the potential to enhance postal code security by creating an immutable ledger for tracking deliveries within specific zones. This could reduce fraud and improve transparency in logistics by providing a decentralized, tamper-proof record of each package's journey from sender to recipient. Blockchain can also help in verifying the authenticity of addresses and preventing "address spoofing," where fake addresses are used for fraudulent activities.
For example, in e-commerce transactions, blockchain could ensure that each step of the delivery process is documented and secure, reducing disputes over lost or undelivered goods. Additionally, blockchain's transparency can be leveraged to build customer trust, showing a clear chain of custody for sensitive or valuable items.
Global Variations in Postal Code Usage
Different countries have tailored their postal codes to their unique needs, such as assigning postal codes to specific zones, states, or regions, resulting in a wide range of formats and uses.
United States
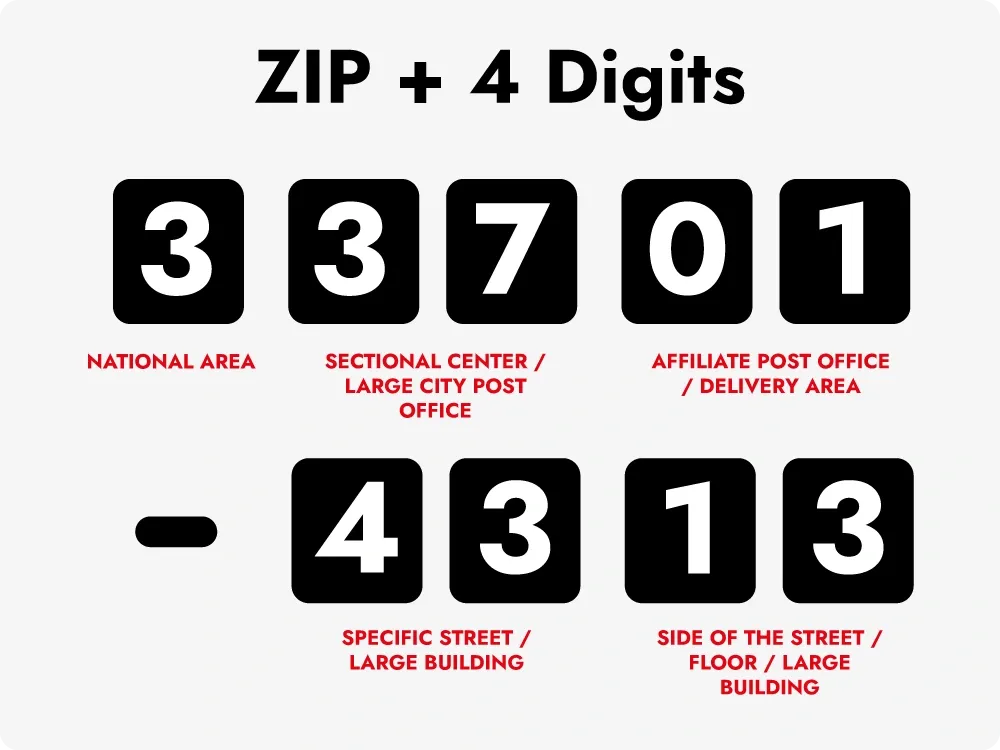
The United States uses a five-digit ZIP code system with an optional four-digit extension (ZIP+4) to identify precise locations for delivery within specific zones. The first digit represents a group of states, the next two digits indicate a central mail processing facility, and the last two digits denote a specific post office or delivery area within a city.
ZIP+4 codes provide even greater precision, identifying specific buildings or delivery points within designated postal zones. This extension is particularly useful for large buildings with multiple tenants, such as office complexes or apartment buildings, where it helps avoid confusion and ensures accurate delivery.
For more in-depth information on the ZIP code system, including ZIP+4, check out our full article on ZIP codes.
United Kingdom
The UK employs an alphanumeric postal code format that provides detailed location information down to individual buildings within specific zones. The code consists of two parts: the outward code (e.g., "SW1A") identifies the postal area and district, while the inward code (e.g., "1AA") pinpoints the specific address.
UK postcodes are designed to be memorable and easy to use. They play a significant role in navigation, with many GPS systems using postcodes to locate addresses within specific city zones. Additionally, the Royal Mail uses postcodes for efficient sorting and delivery, minimizing manual handling and reducing operational costs.
Japan
Japan's seven-digit postal code system starts with three digits representing a prefecture, followed by four digits that specify local areas and post offices within specific zones, ensuring efficient sorting and delivery across the country's 47 prefectures. The system is designed to handle the country's high population density and urban complexity, providing reliable mail delivery even in crowded cities like Tokyo and Osaka.
Japanese postal codes are also used for a variety of non-postal purposes, such as determining regional tax rates, supporting local government planning, and guiding emergency response teams.
Canada
Canada uses a six-character alphanumeric postal code system, such as "K1A 0B1," combining letters and numbers to identify locations with precision. The first letter represents a province or territory, while subsequent characters provide detailed location information down to specific neighborhoods or buildings.
Canadian postal codes are designed to be easy to remember and communicate. They are used in a wide range of applications, from guiding emergency services to demographic studies and urban planning. Canada Post leverages postal codes to offer highly reliable and efficient mail delivery services through its network of post offices across the country's diverse geography.
Future Trends in Postal Code Development
Integration with Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality (AR) could revolutionize how people interact with postal codes. For example, postal workers or delivery drivers could use AR glasses to display digital overlays of postal codes, route information, or even package details within specific zones while looking at physical buildings. This would streamline the delivery process by providing real-time information and directions.
AR could also be used by consumers to visualize nearby services based on postal codes, such as finding the nearest post office, pharmacy, or restaurant. This technology could greatly enhance the efficiency and user experience of both postal services and local businesses.

Enhanced Address Verification Systems (AVS)
The development of more sophisticated Address Verification Systems (AVS) is crucial to the future of e-commerce and digital transactions. Future AVS could integrate AI and machine learning to automatically detect inconsistencies or potential fraud in real-time, providing a much more secure online shopping experience for consumers using credit cards.
These advanced systems could also offer better integration with global postal networks, allowing for seamless international address verification within specific postal zones, which is currently a major challenge for cross-border e-commerce.
Conclusion
Postal codes are essential tools in modern society, facilitating communication, commerce, logistics, and public administration across various zones and cities. As technology continues to advance, their role is set to expand even further, integrating with innovative solutions like AI, AR, and blockchain to improve efficiency, security, and user experience. Understanding postal codes and their applications is key to navigating the interconnected world we live in today.
And if you’re curious to explore your exact location in relation to postal codes, try our Woosmap "Where Am I" tool for a quick and accurate geolocation experience within your specific zone.
About Woosmap
Woosmap empowers businesses to optimize Location Services and Intelligence with precision and efficiency. By leveraging advanced geolocation, Store Locator, and Map API tools, Woosmap ensures accurate deliveries, streamlines address entry processes, and enhances customer satisfaction. With a strong commitment to privacy, Woosmap delivers innovative, GDPR-compliant solutions that do not collect personal data, making it a trusted partner for companies prioritizing both performance and user trust.
